Packing
- 10x10
(Alu-Alu)
MRP
- 72
Overview
TELEMIF belongs to a class of medicines known as angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Angiotensin II is a substance produced in your body which causes your blood vessels to narrow, thus increasing your blood pressure. TELEMIF blocks the effect of angiotensin II so that the blood vessels relax, and your blood pressure is lowered.
WHAT IS TELEMIF AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR?
TELEMIF is used to:- Treat high blood pressure (also called hypertension)
- Prevent cardiovascular complications, including death due to cardiovascular causes, in patients older than 55 years of age with coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, previous stroke, previous transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or high risk diabetes with evidence of end organ damage.
Why is this medication prescribed?
TELEMIF is used to treat essential hypertension (high blood pressure) in adults. 'Essential' means that the high blood pressure is not caused by any other condition. High blood pressure, if not treated, can damage blood vessels in several organs, which could lead sometimes to heart attack, heart or kidney failure, stroke, or blindness. There are usually no symptoms of high blood pressure before damage occurs. Thus it is important to regularly measure blood pressure to verify if it is within the normal range. TELEMIF is also used to reduce cardiovascular events (i.e. heart attack or stroke) in adults who are at risk because they have a reduced or blocked blood supply to the heart or legs, or have had a stroke or have high risk diabetes. Your doctor can tell you if you are at high risk for such events.Warnings
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking TELEMIF.
Please tell your doctor if you are suffering or have ever suffered from any of the following conditions or illnesses:
Kidney disease or kidney transplant.
Renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the blood vessels to one or both kidneys).
Liver disease.
Heart trouble.
Raised aldosterone levels (water and salt retention in the body along with imbalance of various blood minerals).
Low blood pressure (hypotension), likely to occur if you are dehydrated (excessive loss of body water) or have salt deficiency due to diuretic therapy ('water tablets'), low-salt diet, diarrhoea, or vomiting.
Elevated potassium levels in your blood.-Diabetes
Contraindications
Telmisartan is contraindicated in conditions like:
Nicorandil and Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Breast Feeding
Adjunct in treatment of Opioid dependence
Dry or painful cough
Side Effects
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Low blood pressure (hypotension) in users treated for reduction of cardiovascular events.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):Urinary tract infections
Upper respiratory tract infections (e.g. sore throat, inflamed sinuses, common cold)
Deficiency in red blood cells (anaemia)
High potassium levels -difficulty falling asleep
Feeling sad (depression) -fainting (syncope)
Feeling of spinning (vertigo) -slow heart rate (bradycardia)
Low blood pressure (hypotension) in users treated for high blood pressure-dizziness on standing up (orthostatic hypotension)
Shortness of breath -cough
Dosage
This is Preferred Dosage:
The recommended dose of telmisartan is one tablet a day. Try to take your medicine at the same time each day. You can take telmisartan with or without food. The tablets should be swallowed with some water or other non-alcoholic drink. It is important that you take telmisartan every day until your doctor tells you otherwise. If you have the impression that the effect of [product name] is too strong or too weak, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. For treatment of high blood pressure, the usual dose of telmisartan for most patients is one 40 mg tablet once a day to control blood pressure over the 24 hour period. However, your doctor may recommend a lower dose of 20 mg or a higher dose of 80 mg. Alternatively, telmisartan may be used in combination with diuretics ('water tablets') such as hydrochlorothiazide which has been shown to have an additive blood pressure lowering effect with telmisartan. For reduction of cardiovascular events, the usual dose of telmisartan is one 80 mg tablet once a day. At the beginning of preventive therapy blood pressure should be frequently monitored. If your liver is not working properly, the usual dose should not exceed 40 mg once daily.
Disclaimer:To be taken only after consulting with the doctor.
Storage
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of that month. This medicine does not require any special storage conditions. Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Telmisartan blocks the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in many tissues, such as vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Its action is therefore independent of the pathways for angiotensin II synthesis.There is also an AT2 receptor found in many tissues, but AT2 is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Telmisartan has much greater affinity (> 3,000 fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor.
Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system with ACE inhibitors, which inhibit the biosynthesis of angiotensin II from angiotensin I, is widely used in the treatment of hypertension. ACE inhibitors also inhibit the degradation of bradykinin, a reaction also catalyzed by ACE. Because telmisartan does not inhibit ACE (kininase II), it does not affect the response to bradykinin. Whether this difference has clinical relevance is not yet known. Telmisartan does not bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and angiotensin II circulating levels do not overcome the effect of telmisartan on blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, peak concentrations (Cmax) of telmisartan are reached in 0.5 to 1 hour after dosing. Food slightly reduces the bioavailability of telmisartan, with a reduction in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of about 6% with the 40 mg tablet and about 20% after a 160 mg dose. The absolute bioavailability of telmisartan is dose dependent. At 40 and 160 mg the bioavailability was 42% and 58%, respectively. The pharmacokinetics of orally administered telmisartan are nonlinear over the dose range 20 to 160 mg, with greater than proportional increases of plasma concentrations (Cmax and AUC) with increasing doses. Telmisartan shows bi-exponential decay kinetics with a terminal elimination half life of approximately 24 hours. Trough plasma concentrations of telmisartan with once daily dosing are about 10% to 25% of peak plasma concentrations. Telmisartan has an accumulation index in plasma of 1.5 to 2.0 upon repeated once daily.Distribution: Telmisartan is highly bound to plasma proteins (> 99.5%), mainly albuminand α1 -acid glycoprotein. Plasma protein binding is constant over the concentration range achieved with recommended doses. The volume of distribution for telmisartan is approximately 500 liters indicating additional tissue binding.
Metabolism and Elimination: Following either intravenous or oral administration of 14C-labeled telmisartan, most of the administered dose ( > 97%) was eliminated unchanged in feces via biliary excretion; only minute amounts were found in the urine (0.91% and 0.49% of total radioactivity, respectively).
Telmisartan is metabolized by conjugation to form a pharmacologically inactive acyl glucuronide; the glucuronide of the parent compound is the only metabolite that has been identified in human plasma and urine. After a single dose, the glucuronide represents approximately 11% of the measured radioactivity in plasma. The cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are not involved in the metabolism of telmisartan.
Total plasma clearance of telmisartan is > 800 mL/min. Terminal half-life and total clearance appear to be independent of dose.
Interactions
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Telmisartan may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how telmisartan/amlodipine works. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- Digoxin
- Lithium medicines used to treat pain and arthritis, called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including COX-2 inhibitors
- Ramipril or other medicines that may be used to treat high blood pressure or a heart problem
- Simvastatin
- Water pills (diuretics)
The FDA categorizes medications based on safety for use during pregnancy. Five categories - A, B, C, D, and X, are used to classify the possible risks to an unborn baby when a medication is taken during pregnancy.
This medication falls into category D. Telmisartan can cause harm or death to an unborn baby. Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant. If you get pregnant while taking telmisartan tell your doctor right away.
For Patient
Information for Patient:
- Take telmisartan exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Your doctor will tell you how much telmisartan to take and when to take it. Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Take telmisartan one time each day at the same time.
- Take telmisartan with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much telmisartan call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
Chemistry
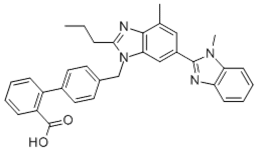
Telmisartan Chemical Name: 4'-[(1,4'-dimethyl-2'-propyl[2,6'-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1'-yl)-methyl]-[1,1'- biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid (IUPAC nomenclature) Structural Formula: Molecular Formula: C33H30N4O2 Molecular Weight: 514.6
Clinical Data
Pregnancy Category | D (Au), D (U.S.) |
Legal status | S4 (Au), POM (UK), Rx-only(U.S.) |
Routes | Oral |